100 100 Answer Cancer Edition Ovarian Question Question Second
Fluid Complications Cancer Network. Malignant Pleural Effusion. Malignant pleural effusion complicates the care of approximately 1. Original Article. Cyclophosphamide and Cisplatin Compared with Paclitaxel and Cisplatin in Patients with Stage III and Stage IV Ovarian Cancer. William P. McGuire, M. Answer Cancer Edition Ovarian Question Question Second' title='100 100 Answer Cancer Edition Ovarian Question Question Second' />The Original Metabolic Medicines Cancer Cure. Dr. Kelleys. DoitYourself Book. Reviewed after 32 years 1967 1999. With. cancer. 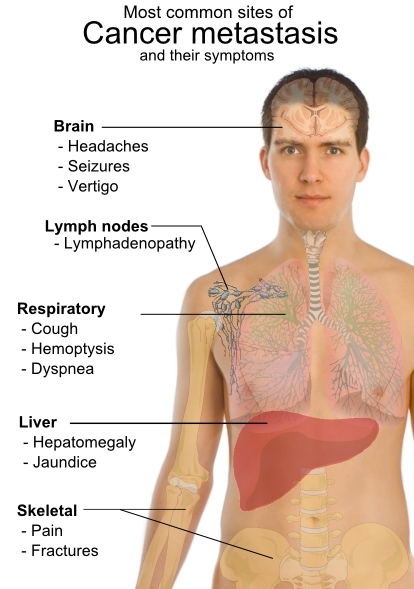 Oesophageal cancer is a clinically challenging disease that requires a multidisciplinary approach. Extensive treatment might be associated with a considerable decline. Incidence and Distribution. The annual incidence of thyroid cancer varies considerably in different registries, ranging from 1. BackgroundTo reduce mortality, screening must detect lifethreatening disease at an earlier, more curable stage. Effective cancerscreening programs therefore both. United States each year. The pleural effusion is usually caused by a disturbance of the normal Starling forces regulating reabsorption of fluid in the pleural space, secondary to obstruction of mediastinal lymph nodes draining the parietal pleura. Tumors that metastasize frequently to these nodes eg, lung cancer, breast cancer, and lymphoma cause most malignant effusions. It is, therefore, puzzling that small cell lung cancer infrequently causes effusions. Primary effusion lymphomas caused by human herpesvirus 8 and perhaps Epstein Barr virus EBV are seen in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome AIDS. Sidebar Stathopoulos et al from Athens, Greece have provided a model to explain why only some cancers result in malignant effusions. They suggest that expression of transcriptional programs leading to higher levels of signaling molecules intrapleurally result in increased permeability. Further interaction with other host cells results in angiogenesis and vascular leakage Stathopoulos GT, et al Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1. Investigators from Tel Hashomer, Israel provide microstructural support for this theory in a study of pleural biopsies from patients with pleural effusion with and without adenocarcinoma. They demonstrate a striking increase in microvessel density. Capillaries and lymphatics are abnormal, displaying changes in normal antigen expression on endothelial cells and pericytes these changes correspond to disturbed vessel wall integrity that is consistent with hyperpermeability Damianovich M, et al Clin Lung Cancer 1. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in these processes is discussed in this chapter. Pleural effusion restricts ventilation and causes progressive shortness of breath by compression of lung tissue as well as paradoxical movement of the inverted diaphragm. Answer Cancer Edition Ovarian Question Question Second' title='100 100 Answer Cancer Edition Ovarian Question Question Second' />Pleural deposits of tumor cause pleuritic pain. Pleural effusions occur more commonly in patients with advanced stage tumors, who frequently have metastases to the brain, bone, and other organs physiologic deficits malnutrition debilitation and other comorbidities. Because of these numerous clinical and pathologic variables, it is difficult to perform prospective trials in patients with pleural effusions. For the same reason, it is often difficult to predict a potential treatment outcome or anticipated duration of survival for the specific patient with multiple interrelated clinical problems. William et al generated survival curves for more than 8,0. NSCLC with pleural effusion ie, stage IIIB from the SEER database and showed that long term survival is uncommon in this group. The median survival time is approximately 3 months. Sidebar Investigators in So Paulo, Brazil studied 2. They noted that pleural effusion causes ventilatory asynchronysometimes so extreme that one lung was inflating while the other was deflating, ie, paradoxical ventilation, immediately reversible with thoracentesis. Advent Aw10 All In One Printer Software Download. The authors reported that after thoracentesis, ipsilateral and contralateral lungs re aerated immediately and without further re aeration over the next hourAlves SH et al Ann Am Thorac Soc 1. Morgensztern et al, from Yale University, used Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results SEER data to identify 5. Answer Cancer Edition Ovarian Question Question Second' title='100 100 Answer Cancer Edition Ovarian Question Question Second' />NSCLC among this group, 9,1. Malignant pleural effusions were associated with larger primary tumors, mediastinal nodal metastasis, and adenocarcinoma. Median survival was better in patients without distant metastasis compared with those who had distant metastasis 5 months vs 3 months, respectively, as were 1 and 2 year survival rates 2. Diagnosis. The new onset of pleural effusion may herald the presence of a previously undiagnosed malignancy or, more typically, complicate the course of a known tumor. Malignant pleural effusions can lead to an initial diagnosis of cancer in patients. In Nantes, France, pleural effusion was the first symptom of cancer in 4. It is important to bear in mind that many cancer patients have comorbid illness and that pleural effusion may have another etiology. Sidebar A group in Bristol, England did CT pulmonary angiograms on consecutive new patients presenting with unilateral pleural effusion in instances in which there was not an immediately obvious cause. Intravenous Vitamin C as Cancer Chemotherapy. Jeffrey Dach MD. Susan is a new patient who wants hormone replacement for relief of menopausal symptoms. Pulmonary embolism was detected in 9 of 1. Hooper C, et al Respiration 8. Thoracentesis. Thoracentesis is the first step in management of almost all cases of malignant pleural effusion. Western Humanities Volume 1 6Th Edition. Ultrasonography facilitates thoracentesis, reduces the rate of complications such as pneumothorax, and can identify pleural nodules andor thickening, suggesting malignant etiology, as well as targeting known lesions for pleural biopsy. An adequate specimen should be obtained and sent for lab studies designed to separate benign and malignant effusions, including cell count determination of glucose, protein, lactate dehydrogenase LDH, and p. H and appropriate cultures and cytology. Chest pressure and pain during thoracentesis can occur when lung elastance is reduced and pleural pressures are markedly negative. Such pain suggests a trapped lung and signals an increased risk of postthoracentesis pulmonary edema. In circumstances in which it is thought desirable to provide continuing drainage of fluid, Seldinger wireguided placement of small bore catheters have largely replaced larger chest tubes. Cafarotti et al described the use of 1. F small bore catheter placements in more than 1,0. The Light criteria lactate dehydrogenase LDH 2. UL pleural serum LDH ratio 0. Answer Cancer Edition Ovarian Question Question Second' title='100 100 Answer Cancer Edition Ovarian Question Question Second' />The majority of undiagnosed exudates are eventually diagnosed as malignant, whereas lt 5 of transudates are shown to be caused by cancer. Transudates may be misclassified as exudates following dehydration or diuresis and if there are erythrocytes and LDH in the fluid. Brain natriuretic protein levels are markedly elevated in effusions secondary to congestive heart failure. Sarkar et al have introduced a simple bedside test that allows identification of exudative effusion at the time of thoracentesis. They add 1. 0 m. L of 3. L of pleural effusion. When catalase is present exudates, the effusion foams. None of 3. 2 transudates produced foam, whereas all 5. Citrix Presentation Server Client For 64-Bit Windows 7 more. The test is not accurate if blood contaminates the fluid. A negative cytology result is not uncommon and does not rule out a malignant etiology. If cytology is negative in an exudative effusion, approximately 2. This low diagnostic yield can be improved by CT or ultrasonographic guidance of needle biopsy. Investigators in Cambridge, England, report that thickening of the pleura 1 cm, pleural nodularity, and diaphragmatic thickening 7 mm on either CT computed tomography or ultrasonography suggest malignant effusion. On positron emission tomography PET scan, a high SUV standard uptake value may indicate a malignant pleural effusion. It is important to note that high SUV values may persist for long periods following talc pleurodesis TP. Metintas et al reported results of a randomized, controlled trial of medical thoracoscopy vs CT guided Abrams pleural needle biopsy for diagnosis in patients with malignant pleural effusions. They studied 1. 24 patients with exudative pleural effusions that were not diagnosed by cytologic analysis. Patients were randomized after CT scan to either thoracoscopy and biopsy or CT guided needle biopsy.
Oesophageal cancer is a clinically challenging disease that requires a multidisciplinary approach. Extensive treatment might be associated with a considerable decline. Incidence and Distribution. The annual incidence of thyroid cancer varies considerably in different registries, ranging from 1. BackgroundTo reduce mortality, screening must detect lifethreatening disease at an earlier, more curable stage. Effective cancerscreening programs therefore both. United States each year. The pleural effusion is usually caused by a disturbance of the normal Starling forces regulating reabsorption of fluid in the pleural space, secondary to obstruction of mediastinal lymph nodes draining the parietal pleura. Tumors that metastasize frequently to these nodes eg, lung cancer, breast cancer, and lymphoma cause most malignant effusions. It is, therefore, puzzling that small cell lung cancer infrequently causes effusions. Primary effusion lymphomas caused by human herpesvirus 8 and perhaps Epstein Barr virus EBV are seen in patients with acquired immune deficiency syndrome AIDS. Sidebar Stathopoulos et al from Athens, Greece have provided a model to explain why only some cancers result in malignant effusions. They suggest that expression of transcriptional programs leading to higher levels of signaling molecules intrapleurally result in increased permeability. Further interaction with other host cells results in angiogenesis and vascular leakage Stathopoulos GT, et al Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1. Investigators from Tel Hashomer, Israel provide microstructural support for this theory in a study of pleural biopsies from patients with pleural effusion with and without adenocarcinoma. They demonstrate a striking increase in microvessel density. Capillaries and lymphatics are abnormal, displaying changes in normal antigen expression on endothelial cells and pericytes these changes correspond to disturbed vessel wall integrity that is consistent with hyperpermeability Damianovich M, et al Clin Lung Cancer 1. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in these processes is discussed in this chapter. Pleural effusion restricts ventilation and causes progressive shortness of breath by compression of lung tissue as well as paradoxical movement of the inverted diaphragm. Answer Cancer Edition Ovarian Question Question Second' title='100 100 Answer Cancer Edition Ovarian Question Question Second' />Pleural deposits of tumor cause pleuritic pain. Pleural effusions occur more commonly in patients with advanced stage tumors, who frequently have metastases to the brain, bone, and other organs physiologic deficits malnutrition debilitation and other comorbidities. Because of these numerous clinical and pathologic variables, it is difficult to perform prospective trials in patients with pleural effusions. For the same reason, it is often difficult to predict a potential treatment outcome or anticipated duration of survival for the specific patient with multiple interrelated clinical problems. William et al generated survival curves for more than 8,0. NSCLC with pleural effusion ie, stage IIIB from the SEER database and showed that long term survival is uncommon in this group. The median survival time is approximately 3 months. Sidebar Investigators in So Paulo, Brazil studied 2. They noted that pleural effusion causes ventilatory asynchronysometimes so extreme that one lung was inflating while the other was deflating, ie, paradoxical ventilation, immediately reversible with thoracentesis. Advent Aw10 All In One Printer Software Download. The authors reported that after thoracentesis, ipsilateral and contralateral lungs re aerated immediately and without further re aeration over the next hourAlves SH et al Ann Am Thorac Soc 1. Morgensztern et al, from Yale University, used Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results SEER data to identify 5. Answer Cancer Edition Ovarian Question Question Second' title='100 100 Answer Cancer Edition Ovarian Question Question Second' />NSCLC among this group, 9,1. Malignant pleural effusions were associated with larger primary tumors, mediastinal nodal metastasis, and adenocarcinoma. Median survival was better in patients without distant metastasis compared with those who had distant metastasis 5 months vs 3 months, respectively, as were 1 and 2 year survival rates 2. Diagnosis. The new onset of pleural effusion may herald the presence of a previously undiagnosed malignancy or, more typically, complicate the course of a known tumor. Malignant pleural effusions can lead to an initial diagnosis of cancer in patients. In Nantes, France, pleural effusion was the first symptom of cancer in 4. It is important to bear in mind that many cancer patients have comorbid illness and that pleural effusion may have another etiology. Sidebar A group in Bristol, England did CT pulmonary angiograms on consecutive new patients presenting with unilateral pleural effusion in instances in which there was not an immediately obvious cause. Intravenous Vitamin C as Cancer Chemotherapy. Jeffrey Dach MD. Susan is a new patient who wants hormone replacement for relief of menopausal symptoms. Pulmonary embolism was detected in 9 of 1. Hooper C, et al Respiration 8. Thoracentesis. Thoracentesis is the first step in management of almost all cases of malignant pleural effusion. Western Humanities Volume 1 6Th Edition. Ultrasonography facilitates thoracentesis, reduces the rate of complications such as pneumothorax, and can identify pleural nodules andor thickening, suggesting malignant etiology, as well as targeting known lesions for pleural biopsy. An adequate specimen should be obtained and sent for lab studies designed to separate benign and malignant effusions, including cell count determination of glucose, protein, lactate dehydrogenase LDH, and p. H and appropriate cultures and cytology. Chest pressure and pain during thoracentesis can occur when lung elastance is reduced and pleural pressures are markedly negative. Such pain suggests a trapped lung and signals an increased risk of postthoracentesis pulmonary edema. In circumstances in which it is thought desirable to provide continuing drainage of fluid, Seldinger wireguided placement of small bore catheters have largely replaced larger chest tubes. Cafarotti et al described the use of 1. F small bore catheter placements in more than 1,0. The Light criteria lactate dehydrogenase LDH 2. UL pleural serum LDH ratio 0. Answer Cancer Edition Ovarian Question Question Second' title='100 100 Answer Cancer Edition Ovarian Question Question Second' />The majority of undiagnosed exudates are eventually diagnosed as malignant, whereas lt 5 of transudates are shown to be caused by cancer. Transudates may be misclassified as exudates following dehydration or diuresis and if there are erythrocytes and LDH in the fluid. Brain natriuretic protein levels are markedly elevated in effusions secondary to congestive heart failure. Sarkar et al have introduced a simple bedside test that allows identification of exudative effusion at the time of thoracentesis. They add 1. 0 m. L of 3. L of pleural effusion. When catalase is present exudates, the effusion foams. None of 3. 2 transudates produced foam, whereas all 5. Citrix Presentation Server Client For 64-Bit Windows 7 more. The test is not accurate if blood contaminates the fluid. A negative cytology result is not uncommon and does not rule out a malignant etiology. If cytology is negative in an exudative effusion, approximately 2. This low diagnostic yield can be improved by CT or ultrasonographic guidance of needle biopsy. Investigators in Cambridge, England, report that thickening of the pleura 1 cm, pleural nodularity, and diaphragmatic thickening 7 mm on either CT computed tomography or ultrasonography suggest malignant effusion. On positron emission tomography PET scan, a high SUV standard uptake value may indicate a malignant pleural effusion. It is important to note that high SUV values may persist for long periods following talc pleurodesis TP. Metintas et al reported results of a randomized, controlled trial of medical thoracoscopy vs CT guided Abrams pleural needle biopsy for diagnosis in patients with malignant pleural effusions. They studied 1. 24 patients with exudative pleural effusions that were not diagnosed by cytologic analysis. Patients were randomized after CT scan to either thoracoscopy and biopsy or CT guided needle biopsy.